900-year-old Ashkenazi DNA ‘shines new light on British Jewish history’
Human remains found in a Norwich well of 17 people, mostly children, suggests they belonged to Ashkenazi Jews who fell victim to antisemitic violence during the 12th century.
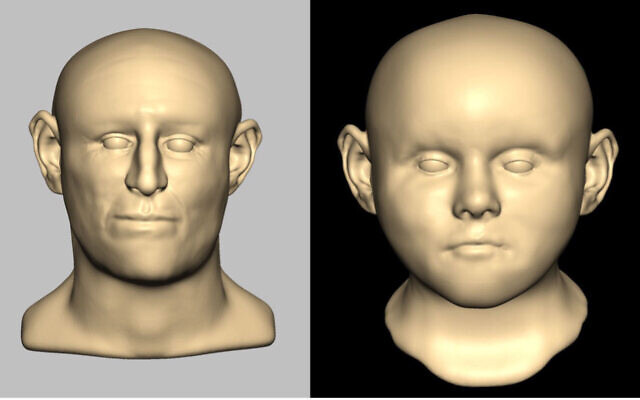
DNA from human remains found in a medieval well suggests they belonged to Ashkenazi Jews who fell victim to antisemitic violence during the 12th century.
In 2004 archaeological excavations in central Norwich uncovered a medieval well containing the remains of at least 17 people, mostly children.
Researchers analysed DNA from six of these individuals, and found strong genetic link with modern Ashkenazi Jews, making them the oldest Jewish genomes to have been sequenced.
According to the study, the findings are consistent with these people being victims of a historically recorded antisemitic massacre by local crusaders and their supporters in Norwich on February 6 1190 AD.
A specific antisemitic riot in 1190 CE was recorded by the chronicler Ralph de Diceto in his Imagines Historiarum II.
He wrote: “Many of those who were hastening to Jerusalem determined first to rise against the Jews before they invaded the Saracens.
Researchers analysed DNA from six of these individuals, and found strong genetic link with modern Ashkenazi Jews, making them the oldest Jewish genomes to have been sequenced.
“Accordingly on 6th February [in 1190 AD] all the Jews who were found in their own houses at Norwich were butchered; some had taken refuge in the castle.”
The findings indicate that four of the probable victims were relatives, including three young sisters (aged 5-10 yrs, 10-15 yrs and a young adult).
Their DNA included variants associated with genetic diseases that are found more commonly in Ashkenazi Jewish – one of two major ancestral groups of Jewish individuals – populations today.
Researchers suggest their study challenges the previous view that disease-related variants associated with Ashkenazi Jewish populations only became more common in the past 600 years.
The researchers also found that they carried markers associated with some genetic disorders for which modern day Ashkenazi Jewish populations are at higher risk.
Genetic disorders particularly common in certain populations can arise during bottleneck events, where a rapid reduction of the population can lead to big jumps in the number of people carrying otherwise rare genetic mutations.
Scientists from the Natural History Museum, University College London, Mainz and Cambridge Universities, and the Francis Crick Institute, conducted analysis on the remains of six of the people discovered at the site.
Unlike other mass burial sites, where bodies are typically laid in an organised fashion, skeletons from the well were oddly positioned and mixed, likely caused by being deposited head-first shortly after death.
Experts suggest these findings hint at mass fatalities such as famine, disease, or murder.
Ancient DNA cannot solve the puzzle of what caused the 17 people to die.
But by working with local historians, archaeologists, and the community, researchers have offered new insights into a significant historical crime, Jewish population history, and into the origins of Ashkenazi-associated genetic diseases.
Dr Selina Brace, a principal researcher at the Natural History Museum and lead author on the paper, said: “I’m delighted and relieved that 12 years after we first started analysing the remains of these individuals, technology has caught up and helped us to understand this historical cold case of who these people were and why we think they were murdered.”
“Nobody had analysed Jewish ancient DNA before because of prohibitions on the disturbance of Jewish graves. However, we did not know they were likely Jewish until after doing the genetic analyses.’
Evolutionary geneticist and co-author Professor Mark Thomas, of University College London, said: “It was quite surprising that the initially unidentified remains filled the historical gap about when certain Jewish communities first formed, and the origins of some genetic disorders.
“Nobody had analysed Jewish ancient DNA before because of prohibitions on the disturbance of Jewish graves.
“However, we did not know they were likely Jewish until after doing the genetic analyses.’
Dr Tom Booth, senior research scientist at the Francis Crick Institute, said: “Ralph de Diceto’s account of the 1190 AD attacks is evocative, but a deep well containing the bodies of Jewish men, women, and especially children forces us to confront the real horror of what happened.”
The findings are published in the Current Biology journal.

Thank you for helping to make Jewish News the leading source of news and opinion for the UK Jewish community. Today we're asking for your invaluable help to continue putting our community first in everything we do.
For as little as £5 a month you can help sustain the vital work we do in celebrating and standing up for Jewish life in Britain.
Jewish News holds our community together and keeps us connected. Like a synagogue, it’s where people turn to feel part of something bigger. It also proudly shows the rest of Britain the vibrancy and rich culture of modern Jewish life.
You can make a quick and easy one-off or monthly contribution of £5, £10, £20 or any other sum you’re comfortable with.
100% of your donation will help us continue celebrating our community, in all its dynamic diversity...
Engaging
Being a community platform means so much more than producing a newspaper and website. One of our proudest roles is media partnering with our invaluable charities to amplify the outstanding work they do to help us all.
Celebrating
There’s no shortage of oys in the world but Jewish News takes every opportunity to celebrate the joys too, through projects like Night of Heroes, 40 Under 40 and other compelling countdowns that make the community kvell with pride.
Pioneering
In the first collaboration between media outlets from different faiths, Jewish News worked with British Muslim TV and Church Times to produce a list of young activists leading the way on interfaith understanding.
Campaigning
Royal Mail issued a stamp honouring Holocaust hero Sir Nicholas Winton after a Jewish News campaign attracted more than 100,000 backers. Jewish Newsalso produces special editions of the paper highlighting pressing issues including mental health and Holocaust remembrance.
Easy access
In an age when news is readily accessible, Jewish News provides high-quality content free online and offline, removing any financial barriers to connecting people.
Voice of our community to wider society
The Jewish News team regularly appears on TV, radio and on the pages of the national press to comment on stories about the Jewish community. Easy access to the paper on the streets of London also means Jewish News provides an invaluable window into the community for the country at large.
We hope you agree all this is worth preserving.